Kubernetes ...
Kubernetes is ...
… providing the building blocks for creating developer and infrastructure platforms but preserves user choice and flexibility where it is essential.
… extensible, and lets users integrate their logging, monitoring, alerting, and many more solutions because it is not monolithic, and these solutions are optional and pluggable.
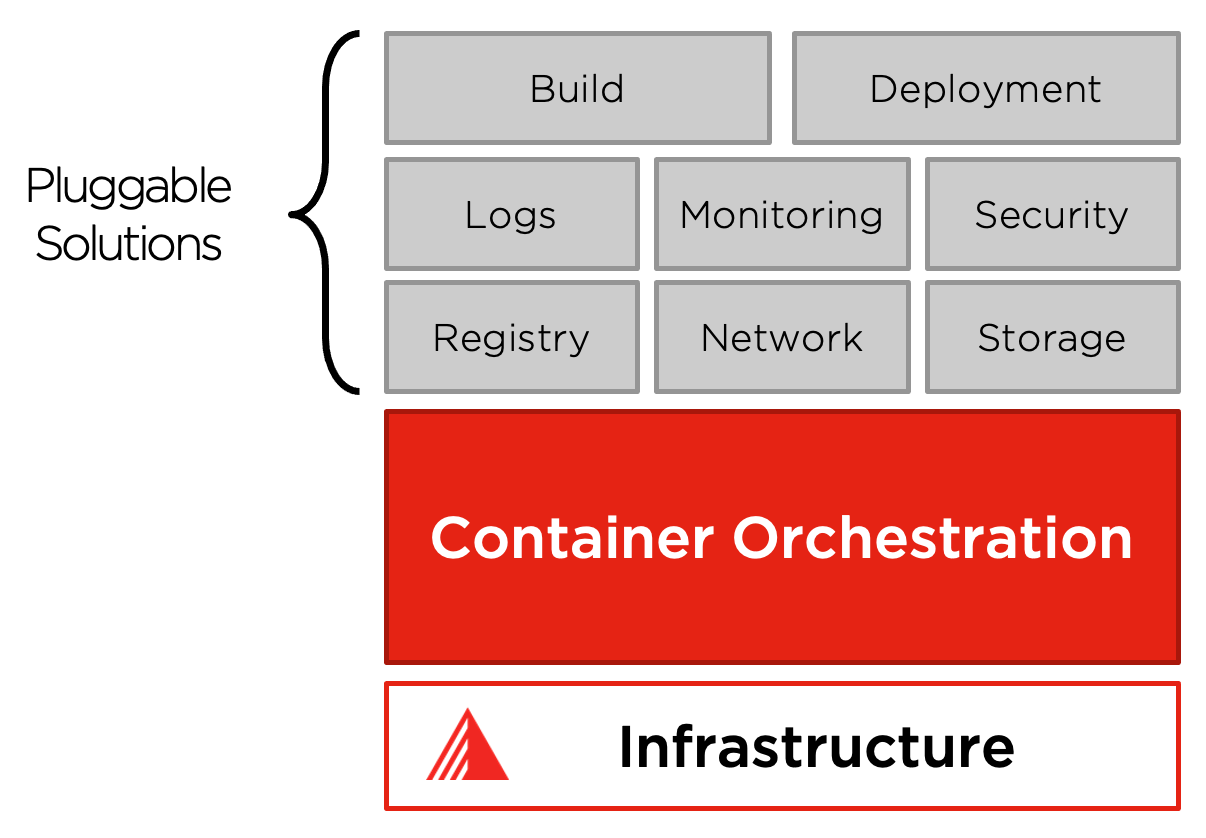
Pluggable Solutions
Kubernetes does NOT ...
… limit the types of applications supported.Kubernetes aims to support a highly diverse workload, including stateless, stateful, and data-processing workloads. If an application can run in a container, it should run great on Kubernetes.
…** deploy source code and does not build your application.**Organizational cultures determine Continuous Integration, Delivery, and Deployment (CI/CD) workflows and preferences and technical requirements.
… provide application-level services.
such as middleware, data-processing frameworks, databases, caches, nor cluster storage systems as built-in services. Application access through portable mechanisms the components mentioned above - both are running Kubernetes.
… provide nor adopt any comprehensive machine management.
The task requires additional components for system configuration, system management & maintenance, etc…
Kubernetes is NOT ...
… a traditional, all-inclusive PaaS system.Kubernetes operates at the container level rather than at the hardware level. It provides some generally helpful features common to PaaS offerings, such as deployment, scaling, load balancing.
… a mere orchestration system.It eliminates the need for orchestration. The definition of orchestration is executing a defined workflow:
Kubernetes comprises independent, composable control processes that continuously drive the current state: